This article provides a basic understanding of what domains are and what knowledge you need for being able to handle domain-related tasks. It also describes the various roles involved in a domain registration process, known as "the three Rs" (Registrant, Registrar, Registry).
What are IP address, domain and TLD?
A simple way to describe a domain is that it's the unique name that identifies a website.
IP address
An IP address, Internet Protocol, is the hosted location of a specific website. The IP address consists of a unique number divided by dots, e.g. 77.66.16.17, which tells exactly where a site is located (hosted).
Domain
There can be multiple websites on the same IP address (location); thus, all websites also have a unique name, a domain, to identify them from each other. The IP address refers to a specific location and the domain name refers to a specific website.
A domain consists of a domain name, a Top Level Domain (TLD) and, in some cases, a sub domain.
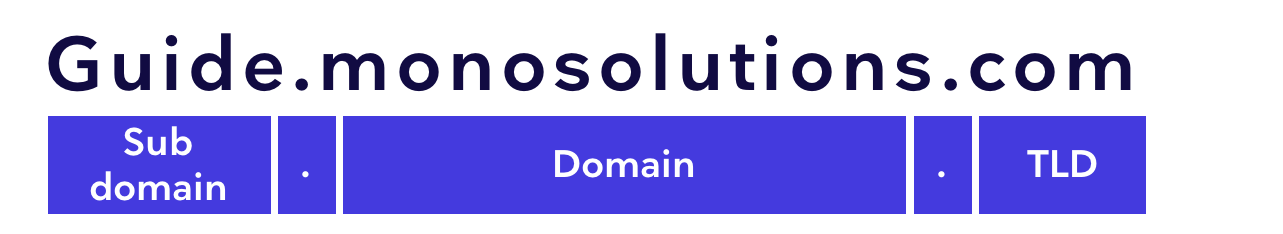
Top level domain (TLD)
Top Level Domains are the highest level in the Domain Name system hierarchy. The TLD determines the general type of domain (e.g. .com, .net, .info, ...). TLDs are typically split into two categories:
1. Generic Top Level Domains (gTLD): Top-level domain with three of more characters, not attached to a specific country.
- .com: commercial and personal sites
- .info: commercial and personal sites
- .net: internet infrastructure companies
- .org: non-profit organizations.
- .mobi: implies that the website is designed for mobile
Rules for creating a domain name with gTLD
It is advised to only use letters, numbers or hyphens ("-"), knowing that it can not begin or end with a hyphen. The entire domain name must have less than 63 characters, not including the TLD, e.g. .com, .net and .org.
2. Country-Code Top Level Domains (ccTLD): Top-level domain with 2 characters, representative of a specific country, for example .de and .fr.
What are the three Rs?
When working with domains, it's important to understand the various people and institutions involved in the registration and management of a domain. We can call them "the three Rs".
- Registrant: The Registrant is the SMB - an individual who has reserved the domain for their own personal or business use. The domain may also have been reserved on their behalf by you as part of a digital service product you've sold to the SMB. In any case, the Registrant is the legal owner of the domain.
- Registrar: A Registrar is the "middle man" - an accredited company who registers the domain on the Registrant's behalf and accepts the payment for the domain. The Registrar also helps you make changes to your domain name after purchase, for example if you need to change your address, payment information or technical information like name servers or DNS settings. When you order a domain through Mono, we place the order with a Registrar. Mono works with a number of different Registrars to help you get the best prices for domains you purchase through Mono.
- Registry: A Registry is a company tasked with the management of domain name registration within the domains for which it is responsible. It also controls the policies of domain name allocation and appoints trusted Registrars to handle the practical registration of domains. Most countries have a single Registry appointed to manage all their ccTLDs, for example DENIC in Germany, Nominet in the UK, and DK Hostmaster in Denmark.
Technical terminology
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| TLD | Top Level Domain. |
| gTLD | Generic Top Level Domain (.com, .net, .org, etc.). |
| ccTLD | Country Code Top Level Domain (.de, .fr, .se, etc.). |
| cPanel | Name for a web control panel to administrate your domain. |
| DNS | Domain Name System. |
| TTL (Time To Live) | Value represented in seconds, telling how often a specific DNS record will update. |
| IP address | Sequence of numbers that represents where the site is located (hosted). |
| Registrant | Domain owner/holder. |
| Registrar | Domain provider - the provider who orders the domain and makes sure that everything works. The direct contact with the Registry. |
| Registry | Different providers for ccTLD's. ICANN is the registry for all gTLD's. |
| Host | Supplier of domains that provides the technologies and services needed for the website to be viewed on the internet. |
| Name servers | Define your domain’s current DNS provider. |